Climate change
initiatives
m-sbAnchor__link
Basic approach
In terms of climate change initiatives, as an entity responsible for stable supply in regions, Mitsuuroko Group aims to harness its comprehensive power embedded in these regions to maintain and improve supply infrastructure to ensure supply is also available during emergencies, while implementing various initiatives that align with the diversification of customer needs and desire for choices.
All of Mitsuuroko Group is engaging in climate change initiatives to achieve a sustainable society through reducing CO2 emissions, promoting renewable energy, and reducing fuel consumption. For customers who are focused on reducing CO2, we offer environmentally friendly electricity plans that stipulate the use of renewable energy. In addition, we utilize monitoring information of remote automatic meter readings, and provide a delivery operation streamlining solution that proposes the optimal delivery plans.
m-sbAnchor__link
TCFD
Mitsuuroko Group’s climate change initiatives
Mitsuuroko Group considers the TCFD recommendations an effective framework for disclosing information and engaging in dialogue with stakeholders in regard to climate change issues. We announce our endorsement of the TCFD recommendations, and in accordance with the recommendations, we disclose information on the impact of climate change on the Group’s business activities and the measures we are taking in response. The Company also participates in the TCFD Consortium*, which discusses initiatives for information disclosure on climate change response in accordance with the TCFD recommendations.
*
The TCFD consortium:
A consortium established in May 2019 and led by the private sector to discuss effective disclosure of information by companies in response to climate change and measures to link the disclosed information to appropriate investment decisions by financial institutions and other parties. The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, the Financial Services Agency, and the Ministry of the Environment participate as observers.

Governance and risk management
The Company recognizes climate change as an important management issue, and the Board of Directors determines policies for addressing climate change and oversees their status.
Specifically, the Director and Group CIDO works together with Inclusion & Diversity, Finance & Control, and Legal & Secretary to analyze materiality, extract and evaluate climate change-related risks and opportunities, and identify material issues concerning such risks.
In addition, the Director and Group CIDO reports periodically (at least once a year) to the Board of Directors on the Group’s risks and opportunities related to climate change as well as their status. Based on these reports, the Board of Directors determines policies and targets (KPIs) for addressing climate change.
For KPIs determined, each department in charge of KPI promotion reports on the progress in a corporate governance report that is submitted monthly to Finance & Control, and Inclusion & Diversity and Finance & Control monitor the progress.
At regular monthly meetings of the Board of Directors, the Director and Group CIDO reports on the status of initiatives based on the policies and targets (KPIs) progress as one of the items in a corporate governance report, and the Board of Directors supervises accordingly.
If new risks or events that may impact the achievement of KPIs are discovered, each department reports on them to the Director and Group CIDO. The Director and Group CIDO then reports to the Risk Management Committee, which is chaired by the Representative Director.
The Risk Management Committee evaluates and analyzes such risks and events, reporting them to the Board of Directors. Based on these reports, the Board of Directors identifies new material issues, then determines policies and targets (KPIs), and supervises them accordingly.
Climate change-related governance and risk management system
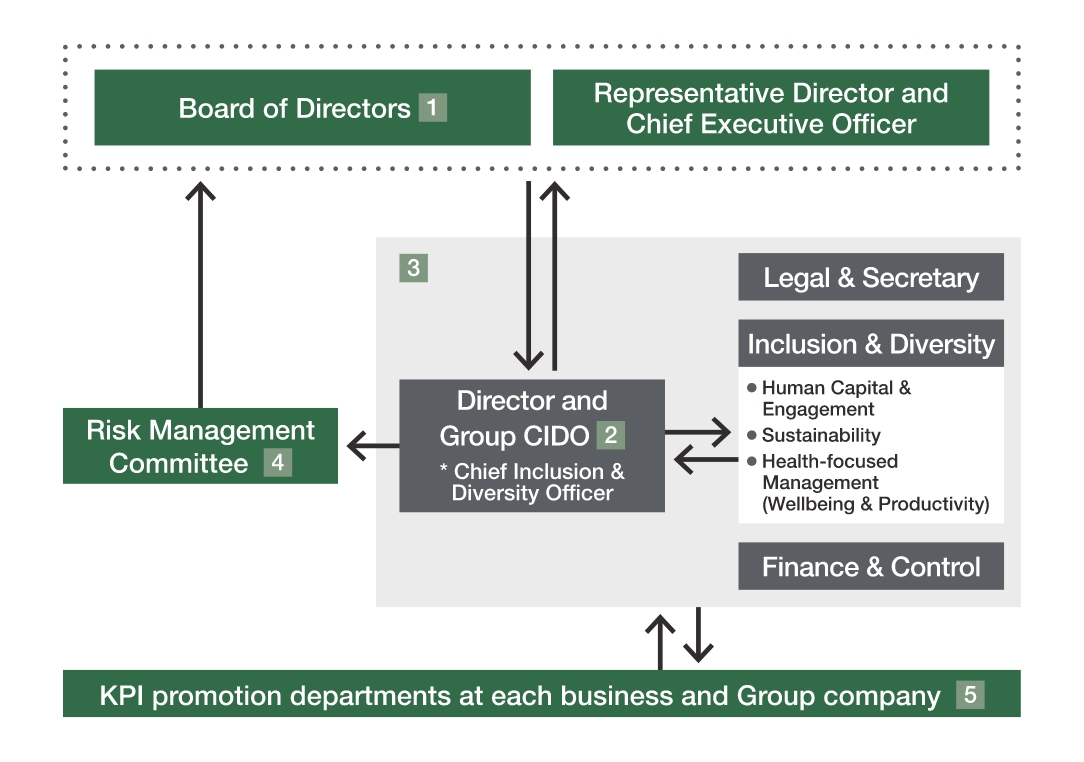
Roles
- The Board of Directors identifies material issues concerning risks and opportunities related to climate change, determines the policies and targets (KPIs) for addressing climate change, and supervises them.
-
The Group CIDO reports to the Board of Directors on risks and opportunities, their status, and progress of KPIs.
If new risks or events that may impact the achievement of KPIs are discovered, they are reported to the Risk Management Committee. - The Group CIDO works together with Legal & Secretary, Inclusion & Diversity, and Finance & Control to extract and evaluate risks and opportunities, and monitor progress of KPIs.
- The Risk Management Committee evaluates and analyzes such risks and events, and reports to the Board of Directors.
- The KPI promotion departments at each business and Group company report on the status of initiatives and progress of KPIs via corporate governance reports to the Board of Directors.
Strategy
The Group assumes climate change to have a significant impact on its Energy Solutions Business and Power & Electricity Business. For these businesses, we have begun analyzing the below 2°C scenario, which is associated with high transition risks, and the 4°C scenario, which is associated with high physical risks.
With 2050 as the target year, we are examining the risks and opportunities that may arise under these scenarios as well as response measures.
The below 2°C scenario assumes that the climate will not change significantly compared to its current state due to the tightening of environmental restrictions. The 4°C scenario assumes that decarbonization and carbon reduction efforts fail to advance, leading to an increase in physical risks such as those due to natural disasters.
Going forward, we will evaluate the impacts under each scenario and also carry out scenario analysis for other businesses, taking the results into account in the formulation of our management plans.
Indicators and targets
The Group’s GHG emissions in FY2021 were approximately 5.99 million t-CO2eq. 99.4% of the emissions were Scope 3, of which 48.8% was attributed to customer gas, electricity, and product usage and 40.3% was attributed to related procurement operations. The Group’s Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions were attributed to vehicle operation (gas delivery vehicles and company cars) and gas and electricity usage within the Company. To reduce the Company’s direct CO2 emissions (Scope 1 and Scope 2), the Group is automating remotely obtained data meter readings for LPG and working to streamline delivery operations (reduction of truck operating time and travel distance), eliminate complicated deliveries, and promote eco-driving activities. We are also changing to electric vehicles (EVs) for company cars and increasing the amount of renewable energy and environmentally friendly energy sources we handle. In addition, to contribute to the reduction of CO2 emissions in our supply chain (Scope 3), we are expanding our meter readings service and delivery operation streamlining services powered by SmartOWL®, transitioning to high-efficiency equipment (ECO FEEL, fuel conversion systems, ECO-JOZU, ECO ONE), and promoting the Mitsuuroko Green Plan.
Breakdown by Scope
|
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions |
Percentage |
CO2 emissions reduction target |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Scope 1 |
★ 17,049t-CO2 | 0.3% | Carbon neutrality by 2050 |
|
Scope 2 |
★ 16,972t-CO2 | 0.3% | |
|
Scope 3 |
★ 5,958,716t-CO2eq | 99.4% |
FY2021 initiatives to reduce CO2 emissions
In the Energy Solutions Business, we have promoted the expansion of our meter readings service and delivery operation streamlining service powered by SmartOWL®, and transitioning to high-efficiency equipment for our existing customers. We are also improving fuel efficiency during deliveries by eliminating complicated deliveries, and shortening travel distances and reducing fuel consumption through eco-driving activities.
In the Power & Electricity Business, we are expanding the provision of the Mitsuuroko Green Plan.
In the Foods Business, we are promoting the sale of label-less PET bottles and the elimination of plastic (use of paper straws and wooden muddlers).
In the Living & Wellness Business, we worked to expand renewable energy electricity contracts in common areas of owned properties and switched to energy-saving equipment and water-saving facilities. We also sold edible container products at the EAS café.(Sales currently suspended) In FY2022, in addition to continuing and expanding the above initiatives, Living & Wellness Business acquired real estate assessor qualifications of CASBEE (Comprehensive Assessment System for Built Environment Efficiency), which is a method for evaluating and rating the environmental performance of buildings. We also changed straws, cups, and cutlery to paper, reduced food mileage*, and promoted production for recycling preform (PET bottle material).
* This thinking focuses on the impact on the global environment of CO2 emitted from the transportation of food. The Company is involved in an initiative to offer products purchased from local stores in Yokohama-shi or vegetables hydroponically grown in the stores.
Climate-related risks and opportunities, and their response measures
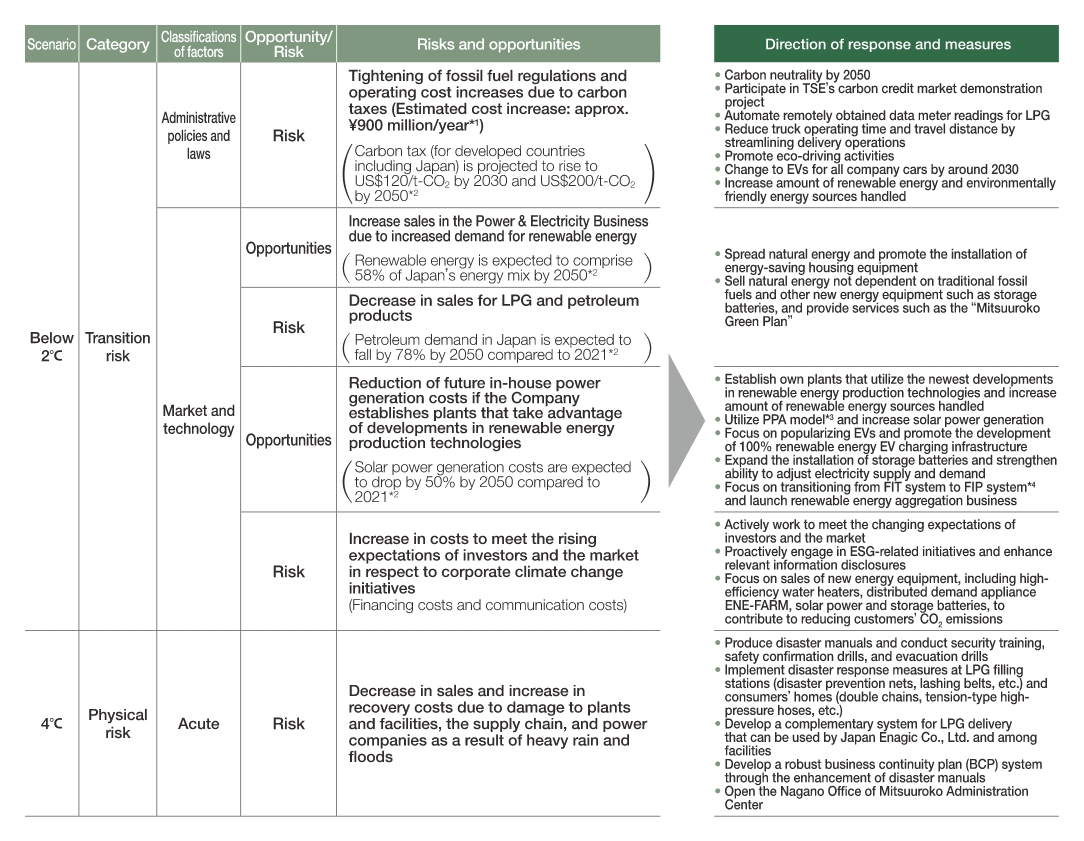
-
The cost increase for business operations due to the impact of carbon tax is calculated as below:
2050 Carbon tax of US$200/t-CO2 is based on the International Energy Agency’s publication, “World Energy Outlook 2022”: Group’s CO2 emissions (t) in 2021 × US$200/t-CO2 × exchange rate (¥/$) - Each estimation is based on the calculations in “World Energy Outlook 2022.”
- PPA model: A business model in which business operators install, manage, and maintain solar power systems on the roofs of consumers’ offices free of charge. Consumers then purchase the electricity that is generated. PPA stands for Power Purchase Agreement
-
FIT: A system where power companies purchase electricity from renewable energy sources at a fixed price for a fixed period of time. FIT stands for Feed in Tariff
FIP: A system where power generation business operators that produce electricity from renewable energy sources and sell it in wholesale markets or through over-the-counter trading are granted a premium equivalent to the difference in the standard price (FIP price) and the market price. FIP stands for Feed in Premium
- TOP
- SUSTAINABILITY
- E(Environment)
- Climate change initiatives